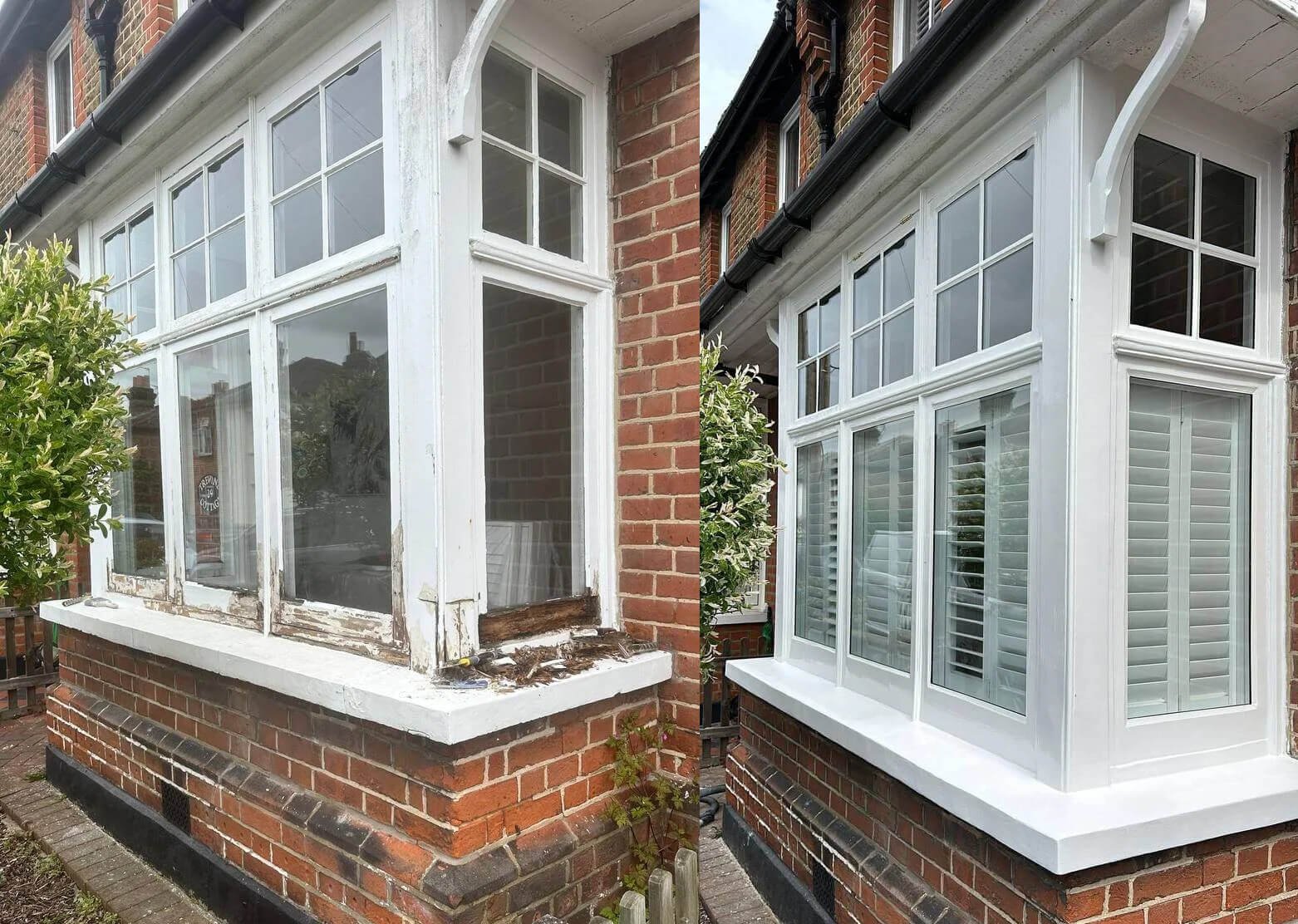
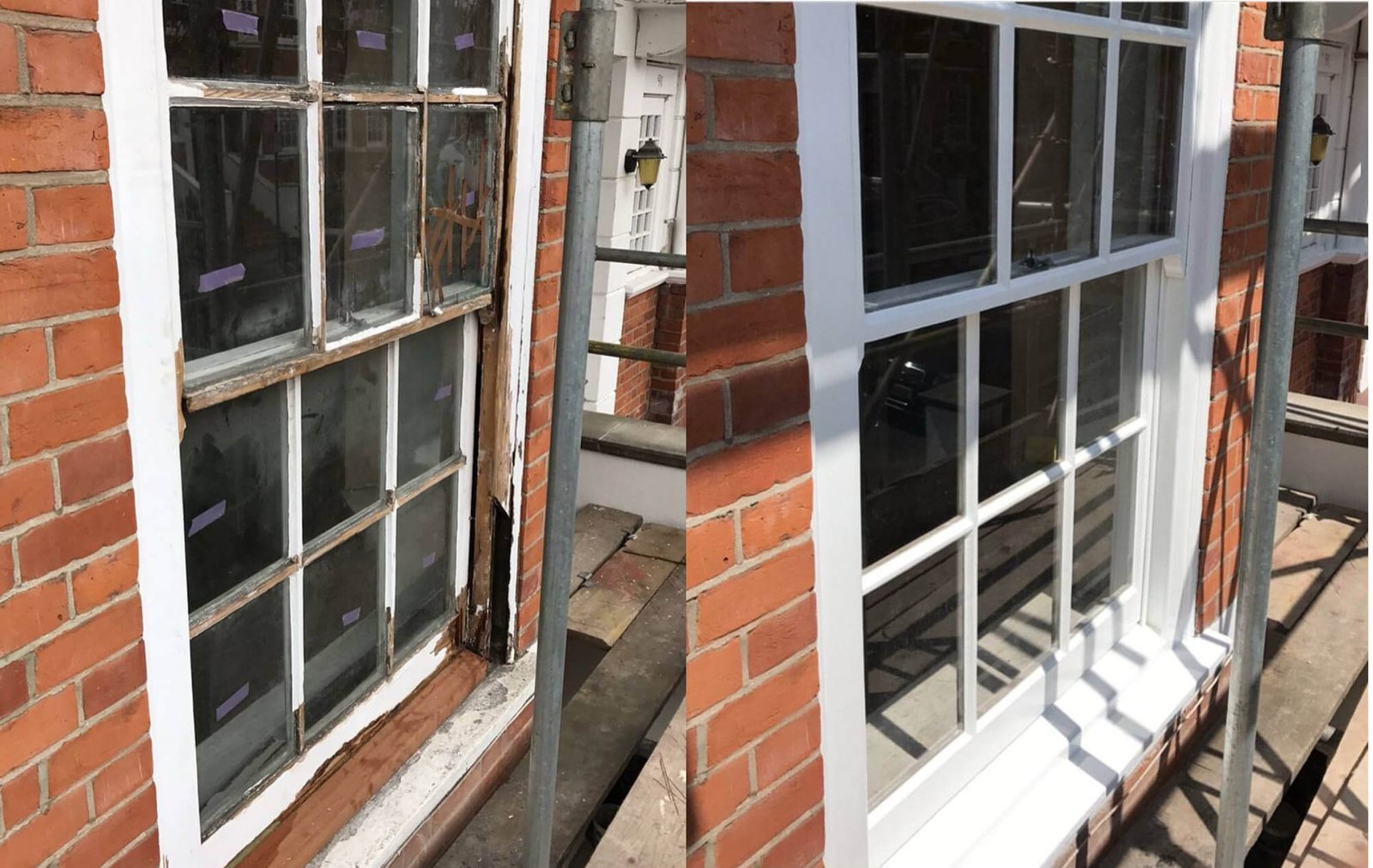
Types of timber used to make timber windows
There are many different types of softwood that are commonly used in the production of timber windows. Some of the most common types include pine, cedar, spruce, and Douglas fir. These softwoods are prized for their strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and rot, making them ideal for use in the manufacturing of window frames.
Pine, softwood
Pine, as we know, is a coniferous wood. Its high resin content prevents premature rotting and allows it to withstand the climatic conditions perfectly. Pine is characterised by its particular strength, lightness and hardness of texture. In the production of pine windows, its wood does not warp in any way and is very easy to work with. Pine windows are highly insulated, many times better than UPVS windows or cheap aluminium windows. Pine windows never freeze due to their high porosity and low specific density. The low weight of pine makes it suitable for large sash windows.
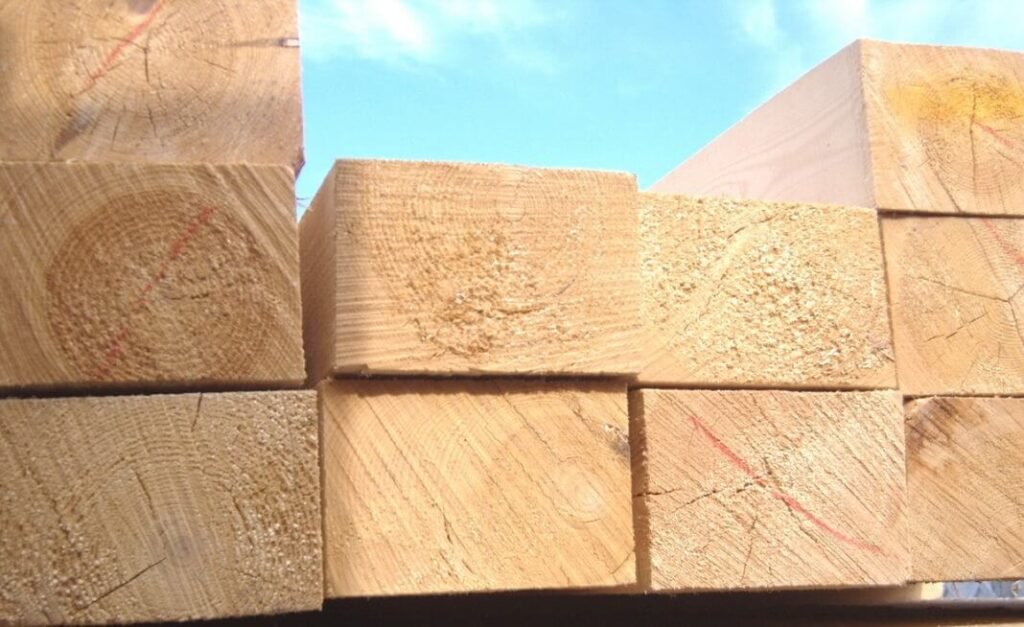


Larch
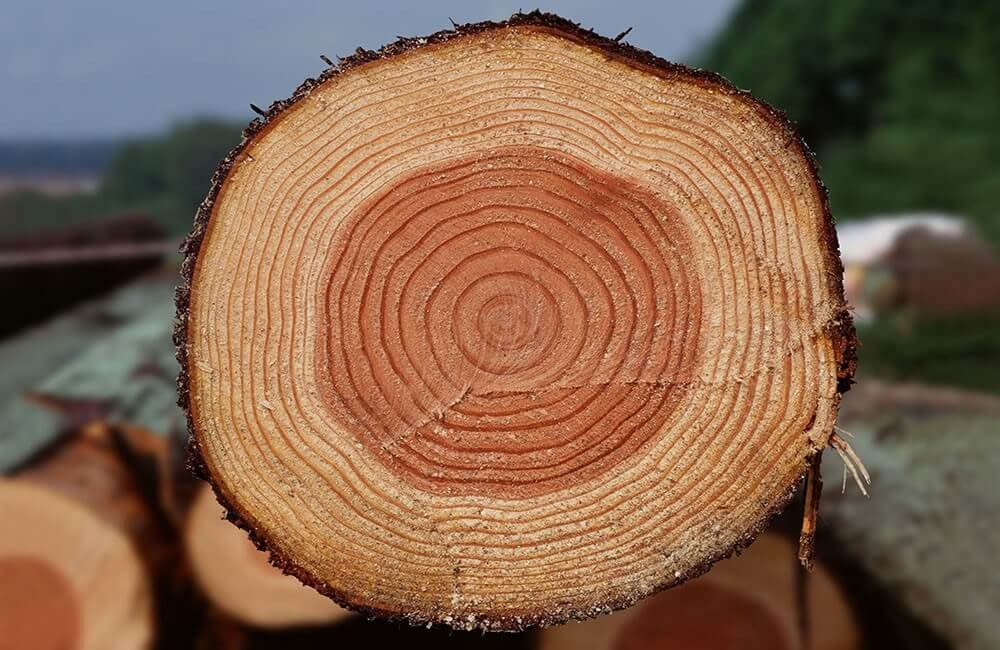

Larch is mainly distinguished by its durability. Larch has three times the strength of pine. Larch is also remarkable for its light brown colour. In addition, this wood has excellent heat conductivity, which allows providing optimal air temperature both in winter and summer. Larch has gum, which is a substance that helps prevent various chemical scouring – rotting, turning blue. It also provides excellent moisture resistance, and moreover, it is not afraid of saltwater. Wood has a resin that repels bugs.

And the antioxidants present in its composition give a person the strength to resist various illnesses and increase emotional strength.
Other softwood species used for making windows
Pine

Pine (Pínus) trees and shrubs in the Pine family (Pinaceae). They are evergreen trees, less commonly shrubby forms, with an erect trunk 30-40 metres in height, 1 metre in circumference with short and long shoots with strictly muscular branching.
- Density 450-500 kg/m3;
Fir

Fir (Abies), is a genus of holospermaceous plants in the pine family. Homogeneous evergreen trees with tall upright trunks (up to 60-80 m tall, diameter up to 3.5 m), with slender pyramidal crown and smooth grey bark bearing resin receptacles; the bark is cracked in old trees. Conifers are perennial, shiny and flat, with a hooked edge, with two whitish stomatal stripes underneath, emarginate at the tip, arranged spirally on the shoots. Microstrobils (male cones) are ovate, located on the upper side of shoots of the previous year, bearing numerous microsporophylls with paired pollen sacs.
- Density 390-430 kg/m3;
Cedar

Cedar pine has an average density of 420 kg/m3. Freshly cut wood high level moister content (109%). When immersed in water, the material can gain up to 220% moisture. The wood is easy to work with and has a low weight due to its medium density. It is more rot-resistant than pine or fir. It does not hold fasteners or other ironmongery as well as pine or fir.
- Density 436-475 kg/m3;
- Compressive strength 33.7-49.2 MPa;
- Shear along fibre 54,1-82,1;
- Tensile strength 28.9-37.1 kJ/m3;
- Compressive hardness 0,077-0,094; Flexural hardness 0,12-0,17.
Oak – hardwood

Oak is of European origin. It is excellent resistance to weather changes, microorganisms and insects. The tannins in the oak wood make it hundreds of times sturdier and harder.
It is oak that has a perfect wood texture. It is not only used for the production of wooden windows with double-glazed sash windows, but also for parquet, furniture, and wooden kitchens.
- Density 690 kg/m3;
Accoya
Accoya a wood made from modified softwood is also becoming increasingly popular for window production and sash window restoration. This treated wood is renowned for its durability and resistance to rot and mould, making it an ideal material for constructing windows that will withstand the test of time. We use this timber in our sash window restoration projects in Surrey.

Accoya wood is made using a process called acetylation. This process modifies the wood’s cell walls, making them more resistant to rot and decay. The acetylation process also makes Accoya wood more dimensionally stable, meaning it is less likely to warp or shrink over time.

To make Accoya wood, the logs are first to cut into lumber and then treated with acetic anhydride. This substance reacts with the cellulose in the wood, creating long chains of acetyl groups that bond to the cell walls. These bonds make the cell walls more resistant to water and decay-causing organisms.
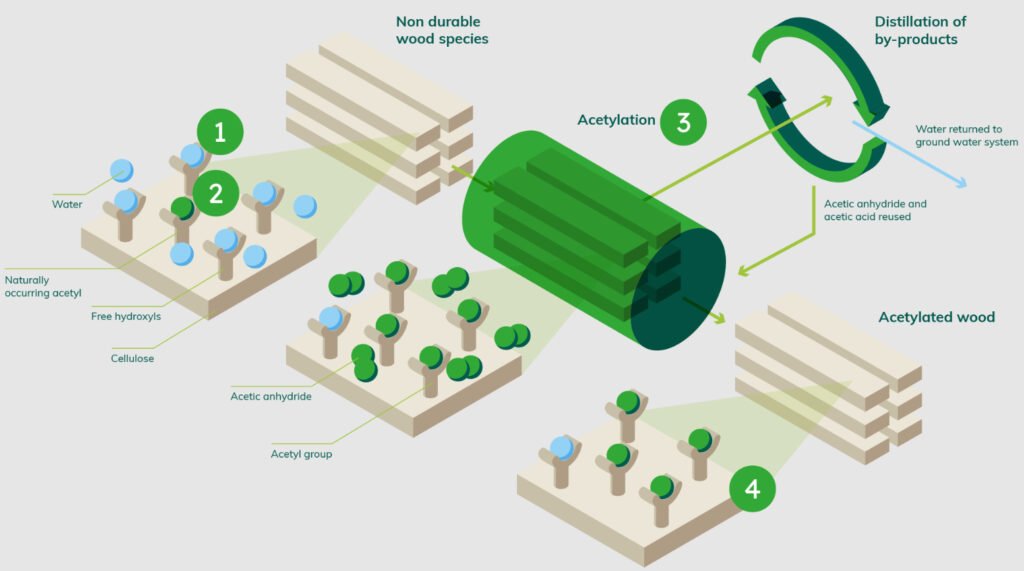
The acetylation process takes place in a controlled environment, where the temperature and humidity are carefully monitored. After the wood has been treated, it is dried and then ready to be used in a variety of applications.
Accoya wood is an ideal material for outdoor use, due to its high resistance to rot and decay. It is also an excellent choice for wooden sash windows.
Density: 420-500 kg/m3;
What is the best timber for the window sill?
There is no definitive answer to this question as it depends on a number of factors, including the climate in which it will be used, and the personal preferences of the individual. Some of the most popular timbers for window sills include cedar, fir, pine, and redwood. Each of these timbers has its own unique properties and benefits, which makes it a suitable material for window sills in different applications.
For example, redwood is known for its durability and resistance to rotting, making it a popular choice for climates that receive heavy rainfall or are prone to high humidity levels. In contrast, pine tends to be less durable but is cheaper.
Wood density of the most common tree species
| № | Wood species | Wood density kg/m³ |
| 1 | Balsa wood | 120-160 |
| 2 | Siberian fir | 390-430 |
| 3 | European spruce | 400-450 |
| 4 | Evergreen Sequoia | 410 |
| 5 | Poplar | 400-500 |
| 6 | Willow | 460 |
| 7 | Pine | 450-500 |
| 8 | Alder tree | 490 |
| 9 | Aspen | 510 |
| 10 | Linden | 530 |
| 11 | Mahogany | 540 |
| 12 | Horse chestnut | 560 |
| 13 | Chestnut | 590 |
| 14 | Cypress | 600 |
| 15 | Bird cherry | 610 |
| 16 | Capelli | 620 |
| 17 | Hazelnut | 630 |
| 18 | Walnut | 640 |
| 19 | Birch | 650 |
| 20 | Cherry | 660 |
| 21 | Smooth elm | 660 |
| 22 | Larch | 660 |
| 23 | Field maple | 670 |
| 24 | Teak | 670 |
| 25 | Pear | 690 |
| 26 | Oak | 690 |
| 27 | Afromosia | 700 |
| 28 | Succulent (mahogany) | 700 |
| 29 | Sycamore | 700 |
| 30 | Joaster (buckthorn) | 710 |
| 31 | Beech | 720 |
| 32 | Hornbeam | 750 |
| 33 | Holly | 750 |
| 34 | Yew | 750 |
| 35 | Ash | 750 |
| 36 | Ducia | 800 |
| 37 | Kempasse | 800 |
| 38 | Plum | 800 |
| 39 | Lilac | 800 |
| 40 | Hawthorn | 800 |
| 41 | Rosewood | 800-1000 |
| 42 | Pecan | 830 |
| 43 | Yarra | 830 |
| 44 | Merbau | 840 |
| 45 | Jatoba (mareil) | 840 |
| 46 | Keruing | 850 |
| 47 | Kulahi | 850 |
| 48 | Muthenia | 850 |
| 49 | Wenge | 900 |
| 50 | Lapacho | 900 |
| 51 | Olive | 900 |
| 52 | Sandalwood | 900 |
| 53 | Panga Panga | 950 |
| 54 | Boxwood | 960 |
| 55 | Lim | 970 |
| 56 | Sukupira | 1000 |
| 57 | Ebony (persimmon tree) | 1080 |
| 58 | Kumaru | 1100 |
| 59 | Ebony | 1160 |
| 60 | Quebracho | 1210 |
| 61 | Guaiacum or Bakaut | 1280 |




